What Are The Diamond Four Cs?
 There are four factors that determine the value of a diamond, collectively known as the 4Cs of Diamonds. The best way to shop for a diamond is to have a good understanding of the 4Cs and determine which factors are most important to you, as each “C” means something different for each individual. For example, some women care most about the carat weight and diamond size, while others might consider the clarity and cut more important. A diamond jewellery purchase should never be based on the specifications alone.
There are four factors that determine the value of a diamond, collectively known as the 4Cs of Diamonds. The best way to shop for a diamond is to have a good understanding of the 4Cs and determine which factors are most important to you, as each “C” means something different for each individual. For example, some women care most about the carat weight and diamond size, while others might consider the clarity and cut more important. A diamond jewellery purchase should never be based on the specifications alone.
Diamond Carat Weight
Carat weight measures a diamond’s weight and size. Because large diamonds are rare, they generally have a greater value per carat.
Diamond Clarity
A diamond’s clarity is affected by any external and internal characteristics created by nature when the diamond was formed or as a result of the cutting process. Learn more about diamond clarity and see diamond clarity charts in this section.
Diamond Color
While the most popular diamonds are colourless, diamonds come in every colour of the spectrum. Diamond colour grades are determined by professionals under ideal circumstances, a situation seldom duplicated outside of a laboratory. Choose a diamond based on its appeal to you, rather than on a technical colour scale.
Diamond Cut
Each diamond is cut to very exacting standards. The cut is one of the most important quality factors of a diamond, as it affects the diamond’s optical and physical properties, like brilliance – how a diamond reflects light.
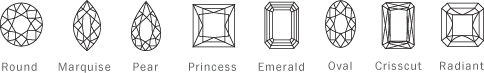
Guide to Diamond & Gem Shapes
Diamonds and gemstones are cut into many different shapes, each with their own aesthetic and cutting requirements. While diamond and gem shapes are sometimes referred to as the cut (for example an emerald-cut diamond), the cut refers to how a jeweller cuts the gemstone to achieve its symmetry and proportion.
Most people are familiar with the round solitaire diamond and common “fancy” shapes — which refer to a gemstone cut in any shape other than round. Fancy cuts include such shapes as baguette, emerald, triangle, pear, princess, oval and marquis. If you are uncertain about a term used to describe your diamond, ask your professional jeweller to clarify it for you.
The Diamond Cut Process
Diamond cut refers to how the jeweller physically cuts the diamond stone into its shape and to the proportions and symmetry that achieve optimal light dispersion, which affects a diamond’s quality and price.
Each diamond is cut to very exacting standards. Let’s look at the process to cut a beautiful diamond to better understand the terminology the jewellery industry uses to explain diamond cut factors.
The most common cut, the round brilliant, has 58 facets, or small, flat, polished planes designed to yield the maximum amount of light reflected back to the viewer.
A diamond’s light reflection, known as brilliance, is an extremely important factor in evaluating the quality of a diamond’s cut. A poorly cut diamond will actually lose light and appear dull.
The widest circumference of a diamond is known as the girdle. Above the girdle of a brilliant cut diamond are 32 facets plus the table, which is the largest and topmost facet. Below the girdle are 24 facets plus the culet, or point.
Proportion diagrams will typically include the following information:
Depth: The height of a gemstone measured from the culet to the table.
Table: Located at the top of the diamond, the table is the largest facet of a diamond.
Girdle: Range of girdle thickness.
Culet: Appearance, or lack thereof, of the culet facet.
A diamond’s cut impacts four aspects of the stone’s optical and physical properties:
Luster: The quality and amount of light that is reflected off just the surface of the diamond. Luster is directly related to the hardness of the stone and the quality of its polish.
Brilliance: The amount of white light that is returned to the eye from both internal and external surfaces. Brilliance is determined by the quality of the diamond’s polish and the number and size of inclusions inside the gem.
Dispersion: The display of spectral or rainbow colours seen coming from the inside of a diamond. Often referred to as “fire,” dispersion is directly related to how well the stone is proportioned.
Scintillation: A diamond will show scintillation, or “sparkle,” when movement is involved. The viewer, the light source or the diamond itself must be in motion for scintillation to occur.
The most important part of choosing a diamond is to choose one that appeals to you personally. While it is beneficial to understand the technical aspects of diamonds, it is most essential to fall in love with your diamond.
Guide to Diamond Color
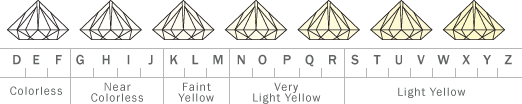
Diamonds come in every colour of the spectrum, but the most popular are colourless. Truly colourless, pure white diamonds are extremely rare and, therefore, the most costly. Laboratories, like the Gemological Institute of America (GIA), grade stones according to how far they deviate from the purest white as one of the diamond 4Cs.
The best way to see the true colour of a diamond is by looking at it against a white surface. Colourless stones are graded D, E or F. All three grades are considered colourless but with slightly decreasing transparency. Colour grading continues down through the alphabet, with each letter designating a slight darkeror warmer tint.
Coloured Diamonds
Diamonds also come in a spectrum of majestic colours, from red and canary yellow to blue, green and purple. These colourful diamonds, known as fancies, are valued for their depth of colour, just as white diamonds are valued for their lack of colour. Therefore, fancy colour diamonds are graded in order of increasing intensity from Faint, Very Light, Light, Fancy Light, Fancy, Fancy Intense, Fancy Vivid, Fancy Dark and Fancy Deep.
Diamond colour grades are determined by professionals under ideal circumstances, a situation seldom duplicated outside of a laboratory. Choose a diamond based on its appeal to you, rather than on a technical colour scale.
Side note
It is important to remember that colour is a range. Think of a diamond colour grade as your age. If you’re 34 years old, your 34th birthday may have been yesterday, or your 35th birthday may be next month. But when someone asks your age, you simply tell them you’re 34. It works the same way with colour grading. For example, a diamond with a G colour grade could, in fact, be very close to an F or to an H.
Guide to Diamond Carats
Carat weight is one of the 4Cs of diamonds that measures measures a diamond’s weight and size. The term “carat” is derived from the carob seeds that were used to balance scales in ancient times.
Today’s metric carat is equal to 200 milligrams, or one-fifth of a gram, and there are approximately 142 carats to an ounce. Carats are further divided into points. There are 100 points in a carat. A half-carat diamond may be referred to as a 50-point stone.
Because large diamonds are rare, they generally have a greater value per carat. When considering the value of a diamond or gemstone, two diamonds or gems of equal carat weight can have differing price points based on the quality of cut, colour and clarity — the three other diamond quality factors.
Diamond Size Chart
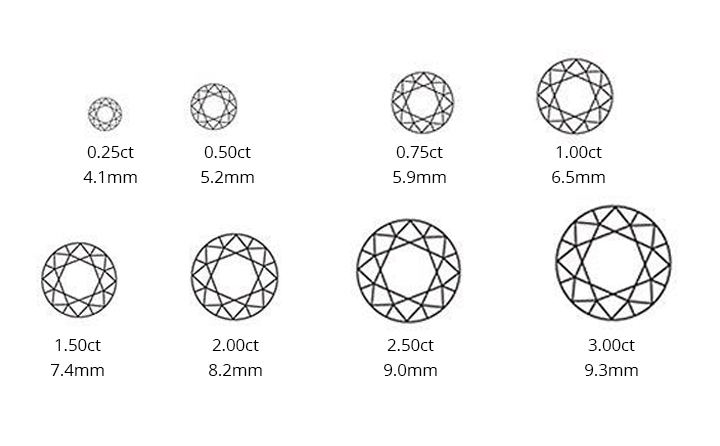
Guide to Diamond Clarity
A diamond’s clarity, one of diamonds 4Cs, is affected by any external and internal characteristics created by nature when the diamond was formed or as a result of the cutting process.
Characteristics such as internal spots or lines are called inclusions. Although these marks make each stone unique, the fewer the inclusions, the more valuable the stone. Inclusions can sometimes interfere with the passage of light through the stone, diminishing the sparkle and value of the diamond.
According to the quality analysis system of the Gemological Institute of America (GIA), clarity is graded on a scale ranging from Flawless (Fl) to Imperfect (I). Only a tiny percentage of diamonds ever achieve a grade of Flawless.
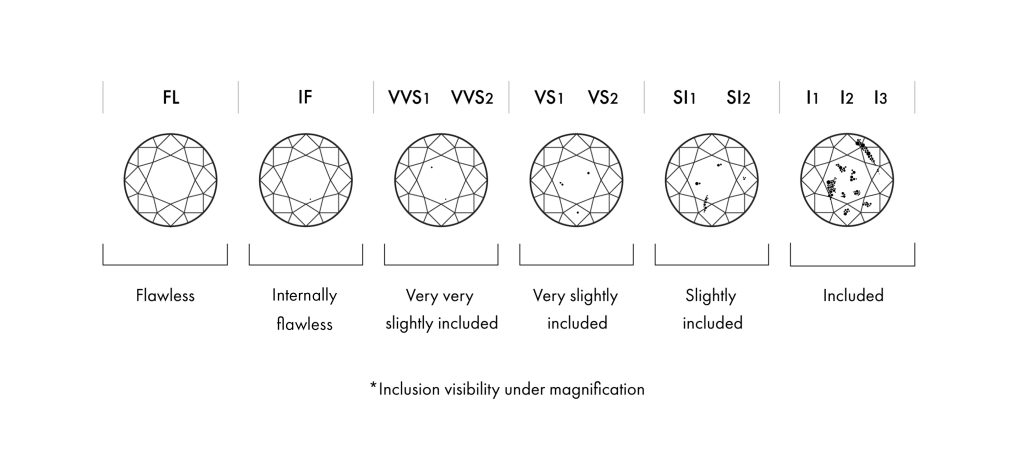 Diamond Clarity Scale
Diamond Clarity Scale
Side note
It is important to remember that clarity is a range. Think of a clarity grade as your age. If you’re 34 years old, your 34th birthday may have been yesterday, or your 35th birthday may be next month. But when someone asks your age, you simply tell them you’re 34. It works the same way with clarity grading.
What’s the difference in 1 carat and 2 carat diamond ?
Have you heard the term “size matters” and we talk about diamonds. It is not an exception. The size of the diamond matters when it comes to engagement rings.
The difference between 1ct diamond ring vs 2ct diamond ring can mean thousands of dollars of cost for your wallet.
So why do most couples choose between these two different sizes? It all boils down to preference and budget— some people prefer larger gemstones while others want something more subtle that blends into everyday life without drawing attention away from themselves. Others just don’t have the budget for a large stone. With so many options available today – including Lab Grown Diamond, choosing the right size could be a big dilemma.
 The Diameter
The Diameter
To begin, just because you buy a 2ct diamond for your ring doesn’t mean that the visual size of your stone will be twice as large as a 1ct. They could actually look similar depending on the cut of the diamond. Diamonds are 3 dimensional objects that carry weight in all ang
les. A diamond’s size can mainly be judged by how it looks from the top. The diameter of a 1ct diamond is 6.5mm compared to 8.2mm of a 2ct diamond. As you can see the 2ct diamond does not have a diameter of 13mm as we would expect and it is because a carat is a weight measurement not a size measurement. The weight of a diamond is measured from all angles. A lot of the weight of a diamond goes into the depth of the stone, (the bottom part) The increase in diameter of a 2ct is only 1.7mm, the difference is 19.5mm square which will give you a 50% more face up compared to a 1ct diamond.
The Price
The price of a diamond can vary in so many ways depending on the colour and clarity of the stone.
A 1ct G-SI1 diamond with excellent cut, excellent polish and symmetry would costs you $6,000, meanwhile a 2ct diamond with similar characteristics would cost you $23,000 there is a large difference of $19,000.
Why is that?
If a 1ct diamond cost $6000 then a 2ct should cost $12,000? The price of a diamond is not based purely in weight but mostly on rarity. The market for 1ct diamonds has more availability than 2ct stones. This means that smaller gems can be sold at lower prices, even though they may lack in terms of size or clarity compared to larger gemstones with the same cut grade (flawless/SI). A FL graded diamond will typically fetch an increased price 2x what would otherwise apply if it were found alongside another stone which had only SI1 certification.
I’m certain you’ll find these numbers fascinating so let me break it down some more: 1ct G-SI1 $6000 vs 1ct G-FL $10,800.
In the past two years, Lab Grown Diamonds have been penetrating the middle class market for couples’ rings to a much greater extent than ever before. People who want a 2ct diamond but don’t have the budget find Lab Grown Diamonds perfect to spend less and increase the size of their stone. For example a 2ct round diamond G-SI only costs $6000 which is the price you pay for a 1ct Natural diamond.
Popularity
The size of your diamonds may be important to you, but so is what they mean. For some women bigger stones represent social status and evidence that he cares while others say it’s all about love with commitment for them – no matter how small the diamond!
Intrinsic value
Many people buy diamonds as an investment. I personally think that a diamond is a symbol of LOVE rather than an investment. If you buy a diamond, once it comes out of the jewellery store you lose at least a 20%. Just like vehicles, once you take the car from the dealer you will not get the same price you paid for. This means when selling your stone to someone else they are unlikely to pay the retail price paid. Diamonds like any other luxury object will only gain appreciation with time if kept for a long term.
When you buy your diamond, don’t see it as something that will triple in price so you can sell it later but more as an investment that will stay in your family for generations.
If you need help with engagement rings and weddings rings, one of the experts at Anania Jewellers would be happy to assist you. Stop into our store or call (02) 9299 4251